Deploy Ceph Cluster with cephadm
Recording how to quickly deploy a Ceph cluster using cephadm.
cephadm is simpler and more convenient compared to ceph-deploy and ansible deployments.
Release version selection:
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/releases/#active-releases
Chose version 18.2.4 for this deployment.
Environment Setup
Prepared 3 machines for this deployment, using Ubuntu 20.04. Specific details:
| hostname | cpu | memory | disk | ip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ceph-node1 | 2 | 4G | 20G, 100G | 192.168.122.50 |
| ceph-node2 | 2 | 4G | 20G, 100G | 192.168.122.51 |
| ceph-node3 | 2 | 4G | 20G, 100G | 192.168.122.52 |
Note this is for testing only - production environments should plan and deploy based on actual requirements.
Set hostnames:
hostnamectl set-hostname ceph-node1
hostnamectl set-hostname ceph-node2
hostnamectl set-hostname ceph-node3Configure hosts:
192.168.122.50 ceph-node1
192.168.122.51 ceph-node2
192.168.122.52 ceph-node3Configure China mirror source, modify /etc/apt/sources.list:
# Default source code mirrors are commented out to speed up apt update, uncomment if needed
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# Pre-release software source, not recommended
# deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# # deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverseUpdate cache after modification:
apt-get updateTime Synchronization
Configure NTP on each node and sync time.
apt-get install chrony -y
systemctl enable chronyd --nowSSH Key Setup
Using ceph-node1 as the main management node, set up one-way passwordless SSH:
ssh-keygenDeploy Docker
Deploy Docker using the official script:
wget -qO- https://get.docker.com/ | shCeph Deployment
Download cephadm
Download cephadm:
CEPH_RELEASE=18.2.4
curl --silent --remote-name --location https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ceph/rpm-${CEPH_RELEASE}/el9/noarch/cephadm
mv cephadm /usr/sbin/
chmod +x /usr/sbin/cephadmDeploy Ceph Cluster
Initialize configuration:
/usr/sbin/cephadm --docker bootstrap --mon-ip 192.168.122.50 --ssh-private-key /root/.ssh/id_rsa --ssh-public-key /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pubAfter deployment completes:
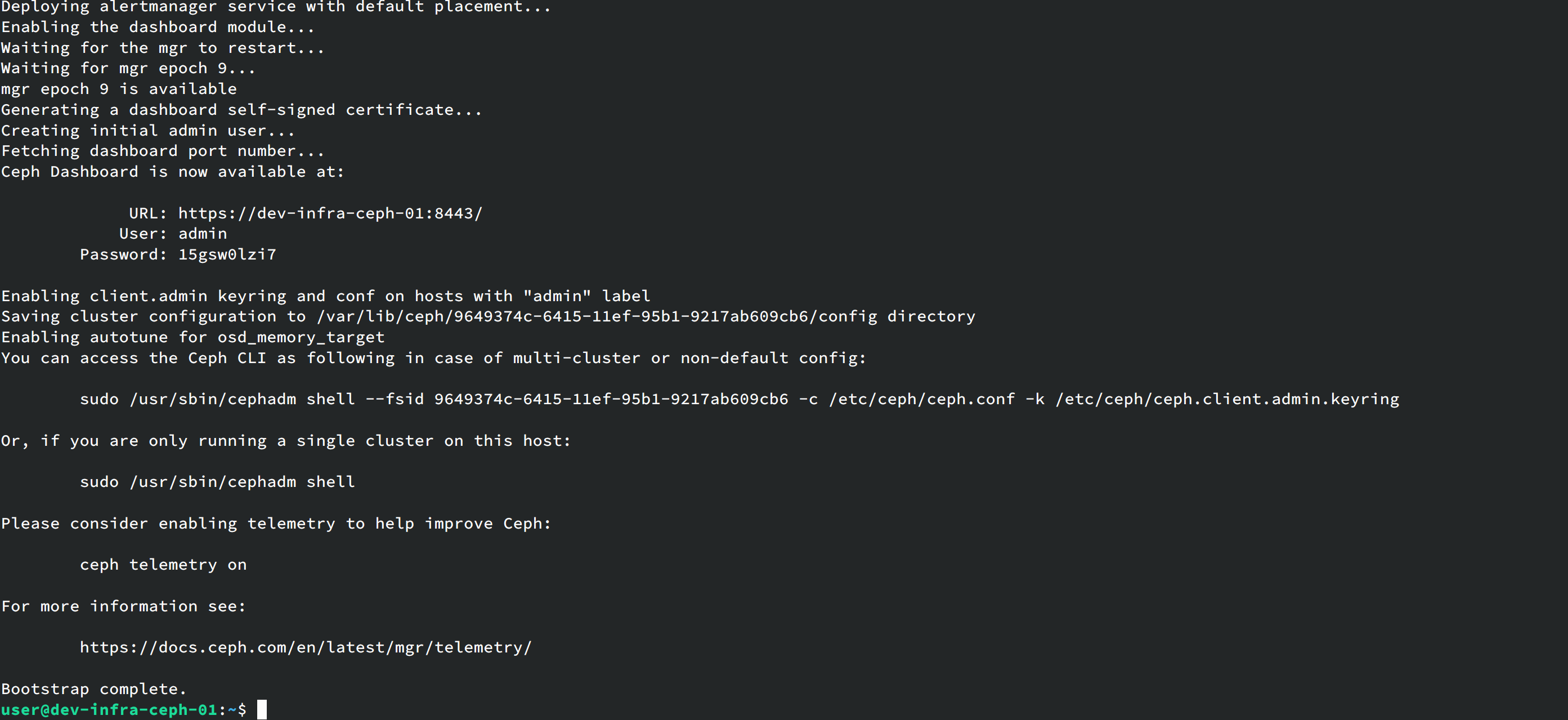
Currently the Ceph cluster is not yet usable. Check cluster status with:
cephadm shell -- ceph -s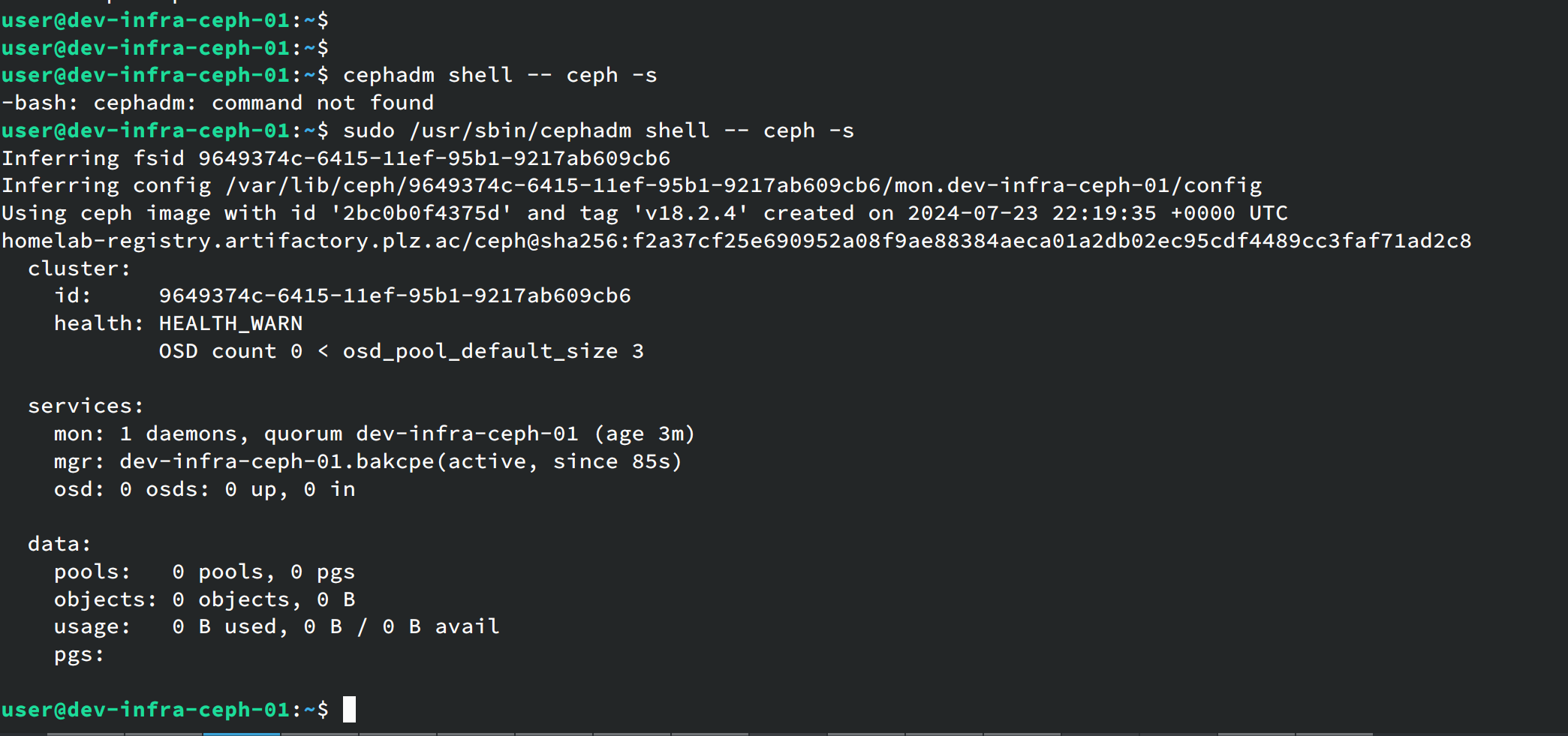
For easier management, install the Ceph package:
cephadm add-repo --release reef
cephadm install ceph-commonAfter installation, check Ceph version:
ceph -vConfigure Ceph Cluster
Check current nodes:
sudo ceph orch host lsDuring initialization we only specified one machine. Add the other two nodes:
sudo ceph orch host add ceph-node2 192.168.56.51
sudo ceph orch host add ceph-node3 192.168.56.52Label the nodes:
ceph orch host label add ceph-node2 _admin
ceph orch host label add ceph-node3 _adminCreate OSDs
Check disk devices on nodes:
ceph orch device ls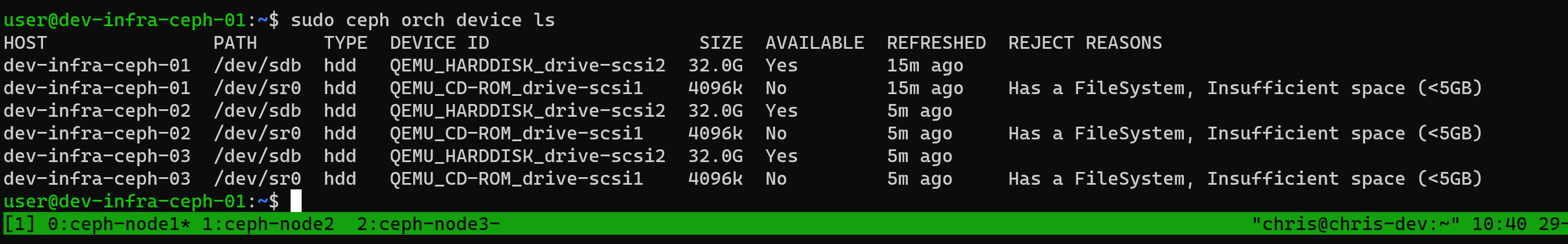
This shows which devices are available and which aren’t.
Add disks:
ceph orch daemon add osd ceph-node1:/dev/vdb
ceph orch daemon add osd ceph-node2:/dev/vdb
ceph orch daemon add osd ceph-node3:/dev/vdbAfter adding, check Ceph status again. The cluster should now show as healthy:
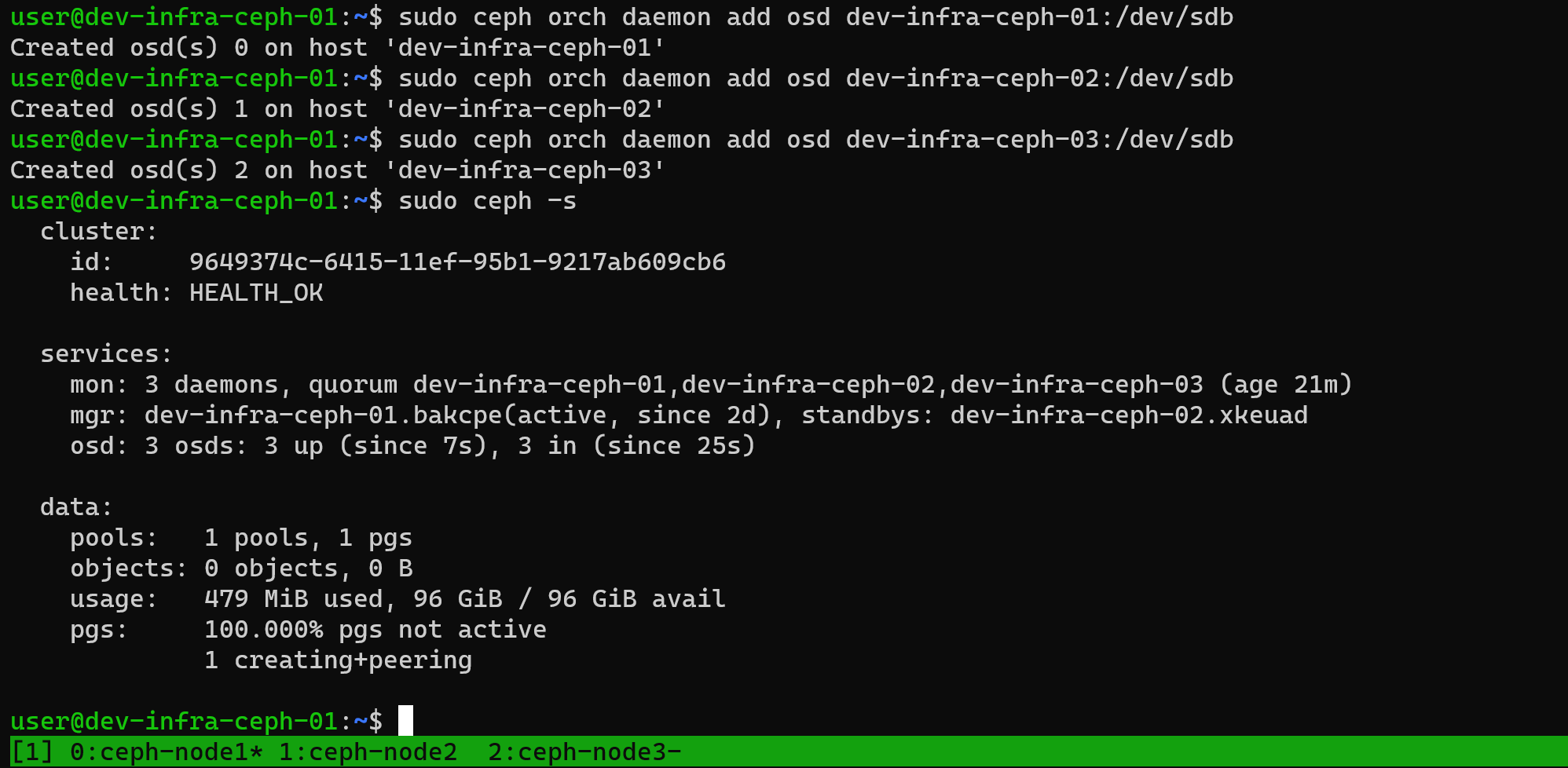
Integrate with PVE
Using RBD storage as example.
Create pool:
ceph osd pool create pveInitialize:
rbd pool init pveCreate authentication:
ceph auth get-or-create client.pve mon 'profile rbd' osd 'profile rbd pool=pve'Save the printed information - you’ll need it when adding to PVE.
In the PVE cluster, add RBD storage with this configuration:
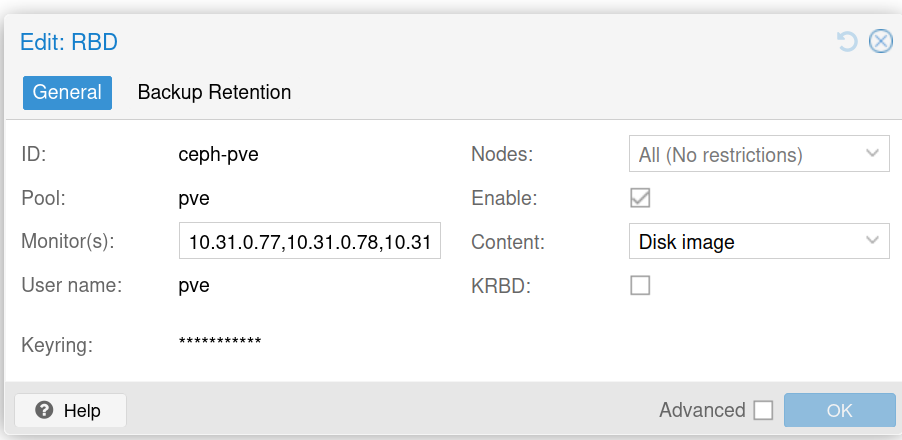
For keyring, use the authorization credential you created.
Integrate with k8s
Create pool:
ceph osd pool create kubernetesInitialize:
rbd pool init kubernetesCreate authorization:
ceph auth get-or-create client.kubernetes mon 'profile rbd' osd 'profile rbd pool=kubernetes' mgr 'profile rbd pool=kubernetes'Get mon information:
ceph mon dumpCreate a namespace for Ceph CSI services:
kubectl create ns ceph-csiGenerate the configmap:
cat <<EOF > csi-config-map.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
data:
config.json: |-
[
{
"clusterID": "2778ca6a-6a9a-11ef-b561-aeb7f1c0facf",
"monitors": [
"192.168.56.50:6789",
"192.168.56.51:6789",
"192.168.56.52:6789"
]
}
]
metadata:
name: ceph-csi-config
namespace: ceph-csi
EOFApply:
kubectl apply -f csi-config-map.yamlKMS configuration - can be set up as needed, skipping for test environment:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
data:
config.json: |-
{}
metadata:
name: ceph-csi-encryption-kms-config
namespace: ceph-csiApply:
kubectl apply -f 02-kms-config.yaml03-ceph-config-map.yaml for Ceph connection authentication:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
data:
ceph.conf: |
[global]
auth_cluster_required = cephx
auth_service_required = cephx
auth_client_required = cephx
# keyring is a required key and its value should be empty
keyring: |
metadata:
name: ceph-config
namespace: ceph-csiApply:
kubectl apply -f 03-ceph-config-map.yaml04-csi-rbd-secret.yaml stores the created credentials:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: csi-rbd-secret
namespace: ceph-csi
stringData:
userID: kubernetes
userKey: xxxx # Replace with your credential keyApply:
kubectl apply -f 04-csi-rbd-secret.yaml05-csi-provisioner-rbac.yaml:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: rbd-csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: ceph-csi
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rbd-external-provisioner-runner
namespace: ceph-csi
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims/status"]
verbs: ["update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshots"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update", "patch", "create"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshots/status"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshotcontents"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list", "watch", "update", "delete", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshotclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumeattachments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumeattachments/status"]
verbs: ["patch"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["csinodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["snapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumesnapshotcontents/status"]
verbs: ["update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["serviceaccounts"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["serviceaccounts/token"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: ["groupsnapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumegroupsnapshotclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["groupsnapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumegroupsnapshotcontents"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["groupsnapshot.storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["volumegroupsnapshotcontents/status"]
verbs: ["update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rbd-csi-provisioner-role
namespace: ceph-csi
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: rbd-csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: ceph-csi
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: rbd-external-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: ceph-csi
name: rbd-external-provisioner-cfg
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["coordination.k8s.io"]
resources: ["leases"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list", "delete", "update", "create"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rbd-csi-provisioner-role-cfg
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: ceph-csi
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: rbd-csi-provisioner
# replace with non-default namespace name
namespace: ceph-csi
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: rbd-external-provisioner-cfg
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioApply:
kubectl apply -f 05-csi-provisioner-rbac.yamlDue to length limits, I’ll note that the remaining files (06-csi-nodeplugin-rbac.yaml, 07-csi-rbdplugin-provisioner.yaml, 08-csi-rbdplugin.yaml, 09-csi-rbd-sc.yaml) should be applied similarly. Key points:
- Update image registry URLs to match your environment
- The StorageClass configuration should reference your cluster ID and pool
- Test with an example pod to verify functionality
Create a test pod:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-with-raw-block-volume
spec:
containers:
- name: fc-container
image: harbor.plz.ac/library/fedora
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args: ["tail -f /dev/null"]
volumeDevices:
- name: data
devicePath: /dev/xvda
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: raw-block-pvcNote: Update the image address to match your registry.
kubectl apply -f 11-raw-block-pod.yamlCheck status:
kubectl get pods
kubectl get pvc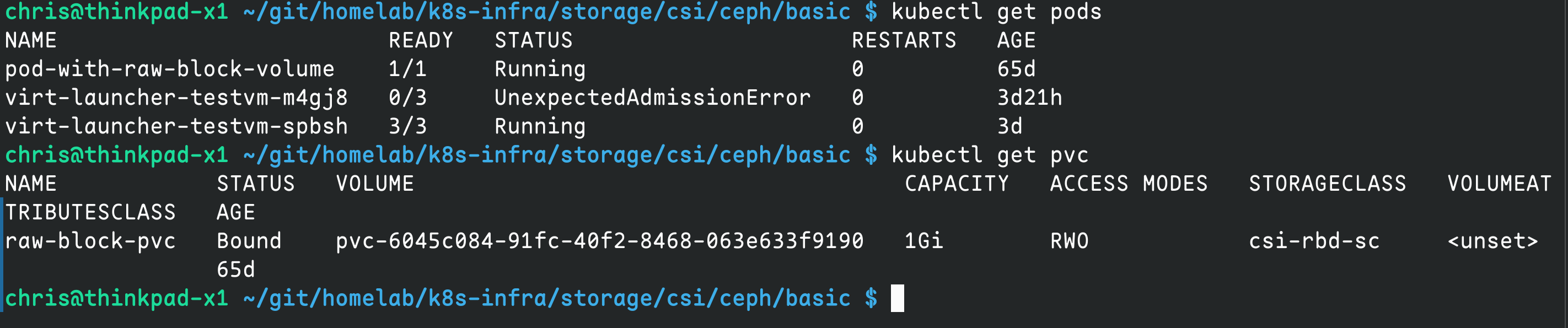
To set as default storage class:
kubectl patch storageclass csi-rbd-sc -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'Rados
Ceph provides object storage with simple configuration.
For HA and security, recommend deploying a separate LB for load balancing. Using nginx here, but you can use other services.
First configure rados with a config file:
service_type: rgw
service_id: homelab
placement:
count: 3
spec:
rgw_frontend_port: 7480This configures RGW on all three nodes with port 7480.
Apply configuration:
sudo ceph orch apply -i homelab.yamlWait about 1 minute then check if the port is bound:
sudo ss -nlp |grep 7480If running, RGW has started successfully.
Configure nginx with a dedicated domain s3.infra.plz.ac:
upstream ceph_rgw {
server 10.31.0.77:7480;
server 10.31.0.78:7480;
server 10.31.0.79:7480;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name s3.infra.plz.ac;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/s3.infra.plz.ac.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/s3.infra.plz.ac.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
location / {
proxy_pass http://ceph_rgw;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header Authorization $http_authorization;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_request_buffering off;
client_max_body_size 5G;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name s3.infra.plz.ac;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}Test and reload nginx:
nginx -t && nginx -s reloadCreate a user:
sudo radosgw-admin user create --uid=infra --display-name="Infra" --email=[email protected]Record the AK & SK. Test with s3cmd:
sudo apt-get install s3cmd -yConfigure s3cmd
vi ~/.s3cfgContent:
[default]
access_key =
secret_key =
host_base = s3.infra.plz.ac
host_bucket = %(bucket).s3.infra.plz.ac
use_https = True
Test:
s3cmd mb s3://demo # create bucket
echo hello > hello.txt
s3cmd put hello.txt s3://demo # upload file
s3cmd get s3://demo/hello.txt # download file
s3cmd del s3://demo --force --recursive # delete all files
s3cmd rb s3://demo # delete bucketMonitoring
Monitoring is installed by default. Access Ceph’s Grafana at:
https://ip:3000
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有所帮助,欢迎赞赏~
Sponsor